Semantic search is not just a feature—it’s the foundation of how search engines interpret queries and rank content today.
In this sixth part of our Semantic SEO series, we’ll decode what semantic search really means, how it evolved from keyword matching, and how it powers Google’s entire search infrastructure in 2025. You will learn why understanding entities, context, and relational databases is essential if you want your content to survive and thrive in the current SEO ecosystem.
“More data = more meaning = better ranking = more revenue — for both Google and you.”
What is Semantic Search?
Definition: Semantic Search = Meaning Over Matching
Semantic search is the process by which a search engine:
- Understands the user’s intent
- Deciphers the context of the query
- Matches it with content using entity recognition and relationship modeling
Unlike lexical search (which matches literal strings), semantic search understands that:
- “MNC vs Liverpool” likely refers to a football match
- “Jaguar” could be a car, animal, or NFL team, depending on context
- “Apple” might mean a fruit, a company, or a device brand

Google no longer sees words.
Google sees entities, nodes, and relationships.
Core Technologies Powering Semantic Search
1. Graph-Based Databases
Google functions as a massive graph database, where:
- Nodes = Entities (e.g., Person, Place, Organization, Product)
- Edges = Relationships (e.g., friend of, located in, founded by)
- Properties = Metadata (e.g., age, population, price, category)
Example:
- Node: “Alice” → Property: Age = 28, City = New York
- Node: “Bob” → Property: Age = 31, City = San Francisco
- Edge: Alice → friend of → Bob
This is how Google stores and retrieves meaning-rich information in milliseconds.

2. NLP (Natural Language Processing)
Google uses NLP to:
- Parse query syntax and semantics
- Identify named entities (e.g., “Apple iPhone 15 Pro Max”)
- Interpret word variations (e.g., “last stop” vs. “final destination”)
- Resolve ambiguity using historical user behavior
NLP + Entity Matching = Understanding User Language with Machine Precision
Traditional Search vs Semantic Search
| Factor | Traditional Search | Semantic Search |
|---|---|---|
| Matching Method | Keywords | Meaning & Intent |
| Focus | Strings | Entities & Relationships |
| Output | Indexed documents | Contextual answers |
| Data Structure | Flat list | Graph-based |
| Tools | TF-IDF, Keyword Planner | NLP API, Schema Markup, Topical Maps |
How Google Processes Semantic Search in Real-Time
A Real Query Example: MNC vs Liverpool
Step 1: Entity Recognition
- MNC = Manchester City
- Liverpool = Football Club
- Query likely refers to a football match
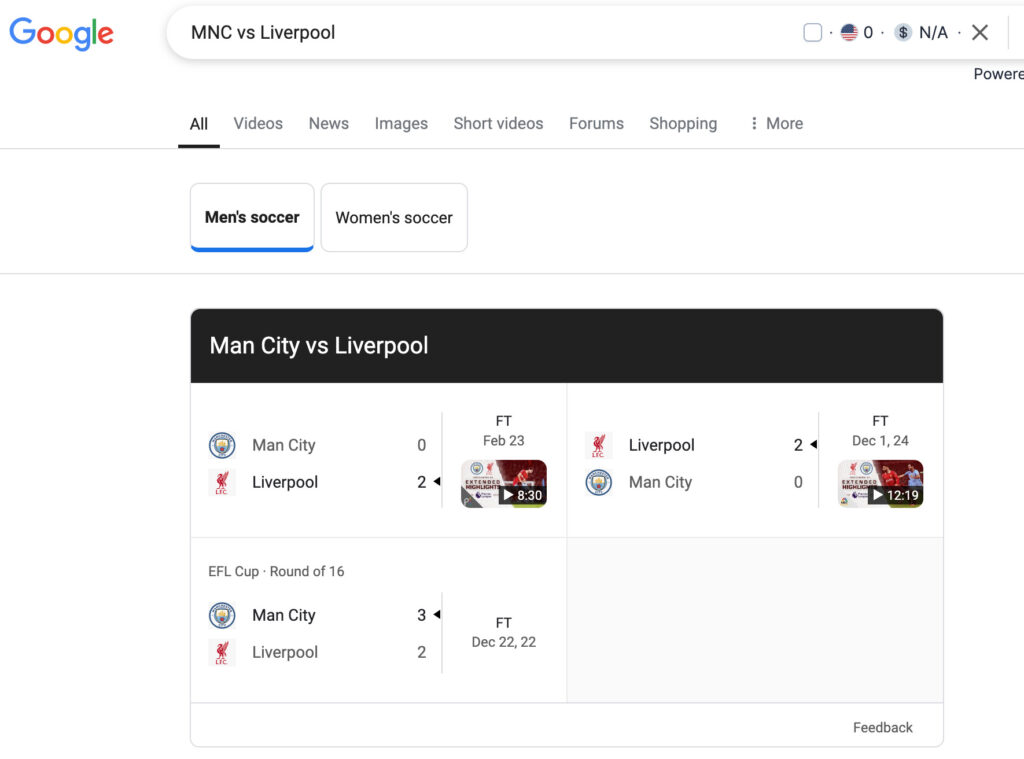
Step 2: Contextual Disambiguation
- Could this refer to city comparisons?
→ No, based on browsing history and regional interest in football
Step 3: Semantic Matching
- Google returns a live match dashboard, not city statistics
- Shows scoreboard, team lineup, related news
Step 4: Result Coloring via Semantic Relevance
- Semantic signals determine:
- What featured snippets to show
- Which Knowledge Graph cards to activate
- What order to rank documents
Semantic Matching in Action
Example: Jaguar
- As a Car Brand: Google prioritizes Jaguar Land Rover
- As an Animal: Image packs or Wikipedia articles
- As NFL Team: Location-dependent SERP triggers team cards

Why? Because Google uses:
- Query context
- User location
- Search history
- Entity graph strength
The Role of Structured Data in Semantic Search
To ensure content is understood semantically, you must:
- Use Schema Markup (JSON-LD)
- Define:
@type: Person, Product, Event, LocalBusinessmainEntity: Core topic of the pagesameAs: External references to trusted knowledge bases
Schema = Communication layer between your content and Google’s entity index.
Key Elements of Semantic Search SEO
| Element | Why It Matters |
|---|---|
| Entity Recognition | Helps Google classify your content meaningfully |
| Relational Modeling | Allows contextual relevance scoring |
| Node-Edge-Property System | Mimics how knowledge graphs work |
| NLP Context Mapping | Ensures intent and syntax are understood |
| Semantic Markup (Schema) | Tells Google what your content is about |
| Topical Maps | Builds domain-level authority around entity clusters |
How to Feed Google’s Graph
The more accurate, rich, and current your data:
- The more semantically aligned your content becomes
- The faster Google can retrieve and rank your pages
- The more trust you build within Google’s knowledge ecosystem
“More structured data = more relevance = more ranking power.”
Update articles.
Add entity data (e.g., price, population, location).
Link entities together.
Use internal linking and external references.
Conclusion: Why Semantic Search is the Future of SEO
Semantic Search transforms SEO from keyword manipulation to meaning construction.
It empowers:
- Personalized search
- Entity-driven results
- Multilingual & multimodal understanding
Google has evolved into a knowledge engine, not just a keyword index.
To survive in 2025, your content must evolve too.
Coming in Part 7: How Do Search Engines Work? A Semantic SEO Perspective on Crawling, Indexing, and Ranking
Disclaimer: This [embedded] video is recorded in Bengali Language. You can watch with auto-generated English Subtitle (CC) by YouTube. It may have some errors in words and spelling. We are not accountable for it.
