In the semantic era of SEO, surface-level tactics like keyword stuffing, backlink purchasing, and thin content creation no longer suffice. To thrive in 2025 and beyond, SEO practitioners must internalize the science of meaning, not just the surface mechanics of search.
Semantic SEO is a discipline that requires:
- Deep understanding of language, structure, and intent
- Familiarity with semantic models like NLP, LSI, and entity salience
- Mastery of technical standards like schema, ontology, and structured data
In this article, we outline what you need to learn, how each element fits into the bigger picture, and why without these components, you’re essentially optimizing in the dark.
The Foundation of Semantic SEO: Meaning, Context & Connection
Before diving into toolsets or workflows, understand the conceptual triad of semantic SEO:
- Deeper Meaning of Words
It’s no longer about matching “cheap flights” with “cheap flights.” It’s about interpreting the user’s actual need—budget-friendly travel options from point A to B within time and price constraints. - Relational Structures Between Words
Relationships are built at every level:- Word → Word
- Word → Sentence
- Sentence → Paragraph
- Paragraph → Document These hierarchies form what we call the contextual web, and optimizing this relationship structure is central to semantic success.
- User Intent Alignment
Every element of content must map directly to a search intent vector: informational, navigational, transactional, or investigational.
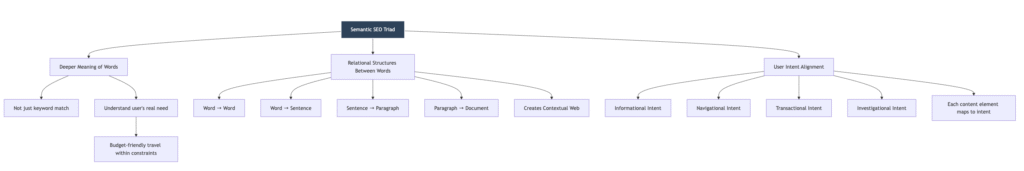
Table: SEO Then vs Now
| Element | Pre-2010 SEO | 2024–2025 Semantic SEO |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Keywords | Entities & Context |
| Optimization | On-page (title, meta, H1) | Semantic Structure, Entity Salience, Topical Depth |
| Ranking Factor | Backlinks | Relevance, Intent Fulfillment, Structured Data |
| Content Format | Isolated Pages | Content Networks & Topic Clusters |
| Targeting | Keyword Volume | Search Intent + Entity Graph |
| Search Engine Behavior | Word Matching | NLP & Knowledge Graph Reasoning |
ALSO READ …
- What is Semantic SEO
- Semantic SEO definition step-by-step guide & glossary
- Traditional SEO vs Semantic SEO
- What is AEO (Answer Engine Optimization)
- What is query semantics
What You Must Learn in Semantic SEO (2025 Curriculum)
1. Semantic Search
- Understand how Google retrieves answers, not just documents.
- Study Search Engine Result Pages (SERPs) and analyze entity-driven layouts: Knowledge Panels, Featured Snippets, PAA (People Also Ask), etc.
- Learn how contextual relevance replaces exact-match logic.
2. Entity-Based Optimization
- Learn what an entity is: a uniquely identifiable object in a knowledge base.
- Understand entity salience (how prominent your target entity is in your content).
- Master tools like Google NLP API, Wikidata, and InLinks for entity extraction and optimization.
3. Natural Language Processing (NLP)
- Explore NLP tasks like:
- Named Entity Recognition (NER)
- Semantic Role Labeling
- Sentiment and Contextual Polarity
- Use NLP to model user queries, refine content tone, and match content with real intent.
4. Topical Authority & Topical Maps
- Learn to build a Topical Map:
- Main topic + semantically related subtopics
- Organized hierarchically based on intent
- Use topical coverage to establish authority over a niche or domain.
5. Structured Data & Schema Markup
- Implement
@type,mainEntity,sameAs, andaboutattributes using Schema.org. - Help Google understand what your page is about, who it’s for, and how it relates to the broader knowledge graph.
6. Latent Semantic Indexing (LSI) & Vector Models
- Learn how Google connects related terms without explicit keyword repetition.
- Explore vector space models, word embeddings (Word2Vec, BERT), and term co-occurrence.
Additional Key Concepts & Jargon You Must Master
Lexical Semantics
- Study of word meanings and relationships (synonyms, antonyms, hyponyms).
- Critical for content diversity and avoiding keyword cannibalization.
Frame Semantics
- Understanding concepts through the frames they invoke.
- Example: “Buying a car” vs. “Purchasing a vehicle” → different tone, same frame.
Distributional Semantics
- Words used in similar contexts have similar meanings.
- Enables automatic discovery of related entities.
Contextual Domains
- Define subject-specific knowledge boundaries.
- E.g., “Python” in tech vs “Python” in biology → different domains, different intents.
Tribute Filtration Framework
Used in entity refinement for content architecture:
- Prominent Tributes: Core attributes (e.g., breed, size)
- Relevant Tributes: Supporting context (e.g., health issues, training)
- Popular Tributes: High-demand queries (e.g., “best dog for kids”)
Supporting Concepts in Semantic SEO
Ontology & Taxonomy
- Ontology: Defines the relationships between concepts (e.g., “a Labrador is a type of dog”).
- Taxonomy: Organizes entities into hierarchical categories.
Internal Linking & Contextual Relevance
- Every internal link should reflect semantic proximity, not just navigation.
- Use contextual anchors to guide crawlers and readers through entity relationships.
Voice Search & Answer Engine Optimization
- 50%+ of searches are now voice-driven.
- Learn to craft conversational content with direct answer structures.
What You Will Build with These Skills
- Semantic Content Briefs: Entity-rich, intent-optimized content plans
- Content Networks: Interlinked topical hubs forming structured authority zones
- Schema-Driven Pages: Pages that teach Google their structure and purpose
- SERP-Ready Answers: Clear, concise, and comprehensive paragraph formats ideal for featured snippets
Conclusion: From Theoretical to Practical – The Semantic SEO Mindset
Semantic SEO is not about keywords anymore. It’s about:
- Understanding meaning
- Mapping context
- Serving intent
- Educating algorithms
To truly master Semantic SEO, you must study deeply, practice consistently, and implement structurally.
“Semantic SEO = Language + Logic + Layout”
— A Modern Framework for Entity-Based Search Optimization
Coming in Part 5: Traditional SEO vs. Semantic SEO – What Changed and Why It Matters in 2025
Disclaimer: This [embedded] video is recorded in Bengali Language. You can watch with auto-generated English Subtitle (CC) by YouTube. It may have some errors in words and spelling. We are not accountable for it.
