Definition: What is EAV?
E-A-V stands for:
- Entity – The distinguishable object or concept (e.g., iPhone 16, Mount Everest, Barack Obama).
- Attribute – A descriptive property or characteristic of the entity (e.g., height, release date, screen size).
- Value – The specific data assigned to that attribute (e.g., 8848m, September 25, 2025, 6.7 inches).
Why it Matters: EAV triples form the semantic spine of structured content. Google doesn’t just rank “content”—it ranks facts and contextual relationships between entities.
What Makes E-A-V Critical in Semantic SEO?
Traditional vs Semantic Content Representation:
| Model | Traditional SEO | Semantic SEO (E-A-V) |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Keywords | Entities + Relationships |
| Structure | Flat text | Rich structured triples |
| Understanding | Term frequency | Contextual graph |
| Indexing | Page-level relevance | Fact-level relevance |
Why Google Prefers E-A-V:
- Enhances entity disambiguation through context (e.g., “running toilet” = malfunctioning hardware, not a mobile restroom).
- Reduces machine processing cost by assigning values directly to attributes.
- Boosts retrieval relevance through structured data (JSON-LD, RDFa, Microdata).
- Powers Knowledge Graph entries, Featured Snippets, and Answer Boxes.
Examples of Entity-Attribute-Value Triples
Example 1: Mount Everest
| Entity | Attribute | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Mount Everest | Height | 8848 meters |
| Mount Everest | Location | Nepal/China |
| Mount Everest | Color | White (ice/snow) |
Example 2: iPhone 16
| Entity | Attribute | Value |
|---|---|---|
| iPhone 16 | Release Date | September 25, 2025 |
| iPhone 16 | Processor | A19 Bionic |
| iPhone 16 | Battery Life | 20 hours (video usage) |
| iPhone 16 | Camera Specs | 48MP Triple Lens |
| iPhone 16 | OS | iOS 19 |
| iPhone 16 | Screen Size | 6.7 inches |
| iPhone 16 | Manufacturer | Apple Inc. |
Each of these is a semantic triple, which Google understands and connects through its internal Knowledge Graph.
Practical Implementation of E.A.V. in SEO
How to Use E-A-V in Content Writing:
Step 1: Identify the Primary Entity with it’s corresponding Attributes and Values
- Example: “iPhone 16”
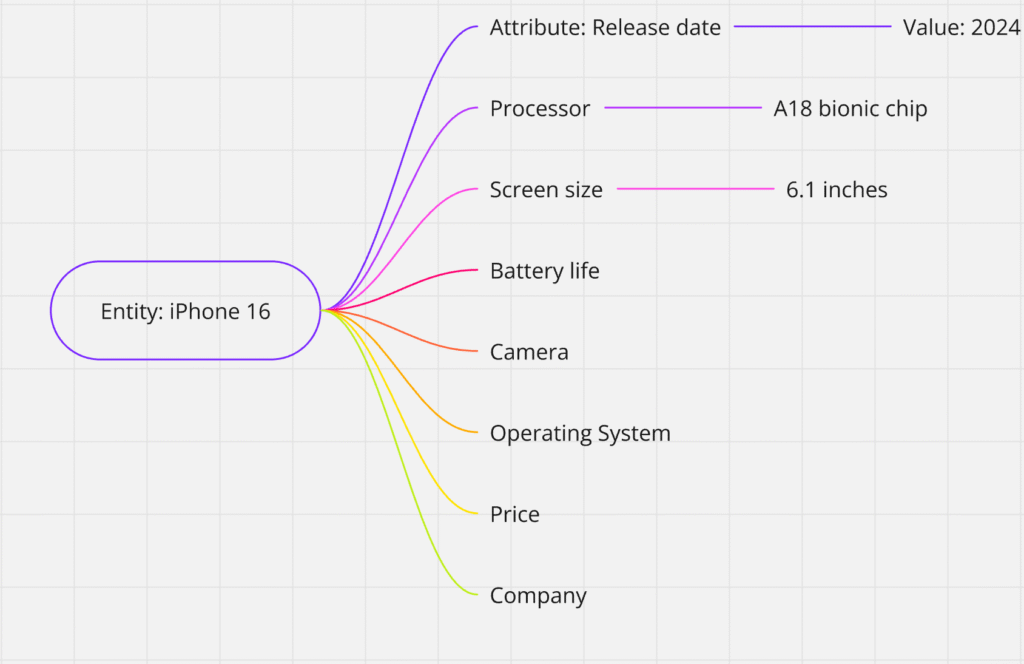
Implement into Content:

Step 2: Map Out Attributes
- Use Google’s Knowledge Graph, Wikipedia infoboxes, or schema.org to find expected attributes.
Step 3: Assign Accurate Values
- Use manufacturer specs, authoritative sources, or first-party research.
Step 4: Structure Using Schema Markup (JSON-LD)
{
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@type": "Product",
"name": "iPhone 16",
"brand": "Apple",
"releaseDate": "2025-09-25",
"offers": {
"@type": "Offer",
"priceCurrency": "USD",
"price": "1299"
},
"additionalProperty": [
{
"@type": "PropertyValue",
"name": "Processor",
"value": "A19 Bionic"
},
{
"@type": "PropertyValue",
"name": "Battery Life",
"value": "20 hours"
}
]
}ALSO READ …
- What is entity and its types
- What is attribute and its types
- What is structured data
- What is entity-based content
- How Google uses entities after extraction
Benefits of Using E-A-V in Semantic SEO
| Benefit | Impact |
|---|---|
| Improves Entity Clarity | Aids Google in disambiguation |
| Enables Rich Results | More CTR via features like snippets |
| Reduces Retrieval Cost | Easier parsing for search engine bots |
| Aligns with Knowledge Graph | Boosts entity associations and context |
| Supports Answer-Based Ranking | Shows up in voice search / Gemini |
Tools for E-A-V and Structured Data
- Schema.org – Attribute and type definitions
- Google’s Structured Data Testing Tool
- Merkle’s Schema Markup Generator
- OpenLink Virtuoso – For RDF and SPARQL queries
- TextRazor / Diffbot / GPT API – For entity extraction
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Using attributes without values (e.g., “Battery Life” with no hours)
- Mixing up attribute types (e.g., using “color” where it’s not relevant)
- Overusing single-value attributes in composite contexts
- Failing to disambiguate the entity in multiple mentions
Final Thoughts
Entity-Attribute-Value (EAV) modeling is not just a database technique. It is the core abstraction model behind Google’s understanding of the world. Every article you write that embeds EAV triples becomes easier to classify, rank, and surface in semantic SERPs.
You’re no longer writing for a keyword-matching engine. You’re writing for a machine that thinks in triples.
Coming in Part 17: How to Find Entities Manually To Do Semantic SEO- Part 17
Disclaimer: This [embedded] video is recorded in Bengali Language. You can watch with auto-generated English Subtitle (CC) by YouTube. It may have some errors in words and spelling. We are not accountable for it.
