Imagine your topic is a cake:
- Knowledge Domain = The whole cake
- Contextual Domain = A slice
- Contextual Layers = The layers in that slice
If your content only gives the top layer (macro), Google says: “Nice, but shallow.”
When you go all the way to micro? Google thinks: “Ah, this site knows the full depth.”
How granular or specific your content goes within that topic.
It’s like a microscope:
- Macro = General topic overview
- Meso = Subcategory or comparative view
- Micro = Ultra-specific instructions, how-tos, use cases
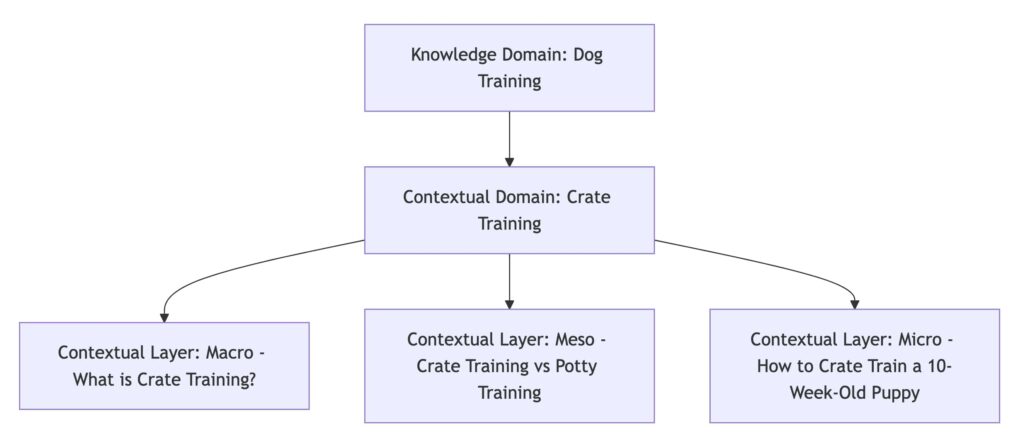
📌 Examples inside Crate Training:
- Macro: What is Crate Training?
- Meso: Crate Training vs Potty Training
- Micro: How to Crate Train a 10-Week-Old Puppy in 7 Days
Definition:
A Contextual Layer is a level of semantic meaning and interpretation added to a piece of content to help search engines accurately classify and rank it based on topic relevance, intent, and entity relationships.
A Contextual Layer is not a separate concept like Knowledge Domain or Contextual Domain — It’s a semantic depth level inside your Contextual Domain, which sits inside your Knowledge Domain.
Think of it like a zoom lens inside a topic.
Zoom = Depth
In the hierarchy of semantic structuring, contextual layers form the most granular level of interpretation. While the knowledge domain defines your topical field (such as dog training or visa consultancy), and the contextual domain defines the interpretive frame within that field (such as crate training or golden visa for Germany), the contextual layer determines the depth, scope, and structural layout of individual pieces of content.
This concept is critical for building content briefs, defining heading structures, and ensuring semantic clarity within a document. It is where you transition from entity-based architecture into search engine-readable structure.
ALSO READ …
- What is contextual domain
- What is knowledge domain
- What is topical map
- Topical map components
- What is topical authority
Knowledge Domain → Contextual Domain → Contextual Layer
To understand the concept clearly, visualize it in three semantic levels:
- The knowledge domain is the broad topic (e.g., Dog Training)
- The contextual domain is a specific segment or angle within the topic (e.g., Leash Training)
- The contextual layer is the breakdown of that specific angle into headings, subheadings, and content clusters
Think of it as a camera:
- Knowledge domain is the entire scene
- Contextual domain is the object in focus
- Contextual layer is the zoom level, angles, and frame composition
Macro, Meso, Micro: The Three Levels of Contextual Layering
A properly designed content structure must include:
| Layer Type | What It Describes | Example (Keyword: “Dog”) |
| Macro Layer | High-level, broad topical context | Dog → Pet, Animal, Mammal |
| Meso Layer | Mid-level specificity, topical cluster scope | Dog → Dog Training, Dog Nutrition |
| Micro Layer | Detail-specific, focused query or feature | Dog → Crate Training → 8-week-old puppy |
Search engines evaluate your content on these layers to determine:
- How well you cover a topic cluster
- How well your content satisfies a specific intent
- How your entities relate to each other contextually
Contextual Layer as Content Outline
The contextual layer can be practically viewed as the content outline:
- H1: Core page topic (macro)
- H2s: Core sections (meso)
- H3s and H4s: Supporting points, entities, values (micro)
For example, a content brief titled “Things to Know Before Moving to Germany” might contain:
- H2: Where is Germany Located?
- H2: What is the Population of Germany?
- H2: What is the Language of Germany?
- H3: German Alphabet
- H3: Telephone Code
- H4: Internet Extension
- H2: What to Pack Before Arrival?
- H2: Major Cities to Visit
Each of these segments is a contextual layer, helping both users and search engines navigate the semantic boundaries of the page.
Table: Full Structure of Contextual Layer
| Knowledge Domain | Contextual Domain | Contextual Layer |
| Germany Visa Consultation | What to Know Before Going to Germany? | Where is Germany on the World Map? |
| Where Does Germany Stand in Mathematics? | ||
| What are Germany’s neighboring countries? | ||
| What are Germany’s borders and border lengths? | ||
| Which Continent is Germany in? | ||
| What is the Surface Area of Germany? | ||
| What is the population of Germany? | ||
| What is the Time Zone in Germany? | ||
| What is the Time Difference Between Germany and Türkiye? | ||
| What is the Language of Germany? | ||
| What is the Spoken Language in Germany? | ||
| Is English Spoken in Germany? | ||
| What Language Is Spoken in Government Offices in Germany? | ||
| What is the German Alphabet? | ||
| What is the International Telephone Area and Country Code for Germany? | ||
| What is the German License Plate Code? | ||
| What is Germany’s Internet Extension? | ||
| What is the abbreviation for Germany? | ||
| What are the cities in Germany? | ||
| What is the Capital of Germany? | ||
| Where is Berlin in Germany? | ||
| What are the places to visit in Germany? | ||
| What is the German Economy Like? | ||
| What is the Currency of Germany? | ||
| What is the National Income Per Capita in Germany? | ||
| What is Germany’s GDP? | ||
| Where Does Germany Rank in the Human Development Index? | ||
| What is the Welfare Level in Germany? | ||
| Where Does Germany Rank in Happiness? | ||
| What is Germany’s Military Power? | ||
| What is Germany’s policy like? | ||
| What is the Government Type in Germany? | ||
| What International Agreements is Germany a Party to? | ||
| Is Germany a Member of the EU? | ||
| Is Germany a Schengen Country? | ||
| Is Germany a Member of NATO? | ||
| What are the symbols of Germany? | ||
| What does the flag of Germany look like? | ||
| What is Germany connected to? | ||
| What are the transportation conditions like in Germany? | ||
| What is the Education System Like in Germany? | ||
| What is the Social Structure of Germany? | ||
| What are the cultural characteristics of Germany? | ||
| What is the architectural structure of Germany like? | ||
| What is German Cuisine Like? | ||
| Who are the Famous Artists of Germany? | ||
| Three Important German Writers | ||
| Three Important Singers from Germany | ||
| What Are the Crime Rates in Germany? | ||
| What Are Living Conditions Like in Germany? | ||
| What Religions Are Believed In Germany? | ||
| What are the 3 Major Events in German History? | ||
| What are the landforms of Germany like? | ||
| What is the climate like in Germany? | ||
| What Other Countries Are Similar to Germany? | ||
| Where is the Turkish Consulate in Germany? | ||
| How to Get to Germany? | ||
| What are the documents required to go to Germany? | ||
| Language Schools in Germany | ||
| Life in Germany |
Content Briefs and Contextual Layering
When creating a content brief using Semantic SEO, you are essentially defining the contextual layers:
- What entities must be covered?
- What questions need to be answered?
- What order should be followed?
- How should these be nested within one another?
A poorly layered content piece may lead to ambiguity.
For example, mixing attributes of an entity with unrelated semantic paths will confuse both readers and NLP models. Proper contextual layering ensures semantic precision, intent satisfaction, and crawl efficiency.
Semantic Depth and Entity Relationships
Contextual layers are the execution mechanism of entity-based content. Every entity carries:
- Attributes
- Values
- Related concepts
Google uses NLP to detect how these entities are:
- Defined
- Connected
- Nested
By explicitly structuring your contextual layers around these entity relationships, you help Google classify content into the correct knowledge domain and contextual domain.
Contextual Layer vs Contextual Domain
These two are not the same.
- Contextual domain defines what the content is about
- Contextual layer defines how the content is organized and interpreted
Example:
- Contextual Domain: Dog Crate Training
- Contextual Layer:
- What is crate training?
- Benefits of crate training
- Crate training by age
- Common mistakes
- Step-by-step guide for 8-week-old puppies
Without layered structure, the content becomes flat, lacks interpretability, and misses opportunities to send precise semantic signals.
Content Granularity and Semantic SEO
In Semantic SEO, granularity defines how deeply a topic is covered and how clearly it is segmented. The contextual layer provides that granularity.
At the macro level, you define the general purpose. At the meso level, you segment by subtopic. At the micro level, you answer user queries with exact detail.
This is how topical authority is earned—not by creating many shallow pages, but by creating semantically deep, contextually layered documents.
Conclusion
To practice Semantic SEO effectively, your content must not only target the right topic but also be constructed in the right semantic shape.
That shape is built through:
- Defined knowledge domains
- Accurate contextual domains
- Precision-built contextual layers
When these layers are constructed correctly, your content becomes:
- Machine-readable
- Topically relevant
- Semantically consistent
- Contextually complete
Contextual layers bridge the gap between user queries and machine interpretation. They ensure that every document you create is not just optimized but understood.
So Google doesn’t just rank pages for “topics.” It ranks them based on:
- How deeply you cover the topic
- How well you match intent
- How semantically precise the meaning is
Disclaimer: This [embedded] video is recorded in Bengali Language. You can watch with auto-generated English Subtitle (CC) by YouTube. It may have some errors in words and spelling. We are not accountable for it.
