In Semantic SEO, the concept of a knowledge domain extends beyond the traditional definition of a “niche.” While many equate niche with the subject area a website focuses on, the knowledge domain introduces an additional semantic layer, it is a structured and defined field of expertise, recognized by both users and machines.
Understanding and implementing your website’s knowledge domain is critical for aligning with Google’s Knowledge Base, integrating into the Knowledge Graph, and establishing Topical Authority.
What is a Knowledge Domain
A Knowledge Domain in Semantic SEO refers to a structured and defined field of expertise that search engines associate with a particular website, entity, or piece of content. It’s the conceptual boundary within which you organize and publish content to:
- Build topical authority
- Align with Google’s Knowledge Graph
- Improve semantic relevance and rankings
- Reflect a real-world field that users search and interact with (e.g., “Dog Training,” “Dental Health,” “Retirement Planning”)
In simple terms, Knowledge Domain = Niche, but with structured and semantic depth.
A niche refers to the general topic you work on.
For example:
- Dogs
- Finance
- Health
- Electric Vehicles
However, in Semantic SEO, a knowledge domain is not just the topic, it is the contextual boundary within which:
- Your content is published
- Your authority is established
- Your entities are semantically connected
It includes all relevant topics, sub-entities, and relationships tied to the central expertise of your website.
Structured and Defined Expertise
A knowledge domain is defined by two characteristics:
- It is structured, meaning its content is organized around interconnected entities
- It is a field of expertise, meaning the content must remain relevant, focused, and semantically consistent
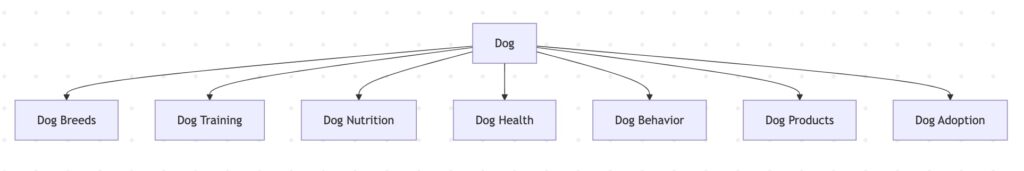
For example, if your site is focused on dog training, the knowledge domain will include:
- Dog breeds
- Dog behavior
- Dog nutrition
- Training techniques
- Accessories
- Veterinary care
Although monetization may be focused on one component (e.g., selling dog training services), publishing content across all relevant topics within the dog domain positions the site as a subject-matter expert. This not only benefits the user but also helps search engines identify the site’s authority.
How Knowledge Domains Align with Google’s Systems
A well-defined knowledge domain aligns your website with three key systems:
Knowledge Base
The Knowledge Base is Google’s internal database where structured factual data is stored. This includes data from sources like:
- Wikipedia
- Wikidata
- Authoritative websites
Publishing accurate, structured content aligned with your knowledge domain helps Google classify your site into this internal database.
Knowledge Graph
The Knowledge Graph is a visual or logical network of entities and their relationships. It is the system Google uses to connect ideas, concepts, and topics.
If your content is semantically consistent and entity-rich, Google can map your content into this graph, allowing your brand or site to appear in knowledge panels or feature snippets.
Example: If your website is about “dog training,” and you cover every topic within that scope, from training types to behavioral issues and health, Google begins to understand your site as a node in its knowledge graph.
ALSO READ …
- What is contextual domain
- What is contextual layer
- What is topical map
- Topical map components
- What is topical authority
Topical Authority
A strong knowledge domain directly feeds into Topical Authority. When Google sees that your site consistently publishes relevant, expert-level content within a defined domain, it begins to prioritize your pages across broader and deeper queries in that space.
This applies not only to the initial topics you target but also to related subtopics and entities.
Examples of Knowledge Domain Structures
Dog Training Website
Central Entity: Dog
Source Context: Training Services
Knowledge Domain Includes:
- Dog breeds (e.g., Labrador, Golden Retriever)
- Dog nutrition (food, supplements)
- Dog behavior (aggression, anxiety)
- Dog health (vaccination, check-ups)
- Accessories (leashes, crates, collars)
The site may only sell training services, but by covering these subdomains, it builds semantic relevance and supports Google’s understanding of the domain.
Visa Consultancy Website
Central Entity: Germany
Source Context: Visa Services
Knowledge Domain Includes:
- Germany student visa
- Germany work visa
- Tourist visa processes
- Legal documentation
- Travel preparation and interviews
By maintaining content within the German visa domain, the website helps Google reinforce topical alignment, thereby enhancing its ranking probability for Germany-related immigration queries.
Thin Knowledge Domains vs Deep Knowledge Domains
Some websites operate in thin or templated knowledge domains:
- Lyrics sites
- Currency converter tools
These sites often repeat the same structure or content format with minimal variation. Google allows these to rank if they meet intent quickly (e.g., currency rate, lyrics lookup), but their topical coverage is shallow.

By contrast, knowledge domains like:
- SEO
- Finance
- Healthcare
Require deep, structured content. Users expect nuance, expertise, and updated insights. Google demands:
- E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authority, Trust)
- Structured topical coverage
- Author identity and credibility
Knowledge Domain, Knowledge Base, and Knowledge Graph: Relationship Explained
- Knowledge Domain: The scope of expertise covered by a website
- Knowledge Base: Google’s database where information from your site can be stored
- Knowledge Graph: A visualized network of how your site’s entities connect to others in Google’s ecosystem
When your content:
- Defines the domain clearly
- Aligns with factual databases
- Connects entities semantically
Google connects your content to its Knowledge Base, maps it into the Knowledge Graph, and begins ranking your site within the appropriate Topical Domain.
Use Case: SEO Industry Knowledge Domain
Let’s say your website focuses on SEO. To define this knowledge domain effectively, you would cover:
- Keyword research
- Technical SEO
- On-page SEO
- Backlinks
- Local SEO
- Content optimization
- Industry updates
These subtopics must be semantically grouped and consistently interlinked. Google will treat your site as a node in the SEO knowledge domain if:
- The content is updated
- It displays expert authorship
- It satisfies query intent
- It contributes to the knowledge graph structure
Understanding Google’s Perception of Knowledge Domains
Google understands different types of content differently:
- For lyrics and currency sites: Minimal variation is expected. The structure is known and standardized. Ranking is based on delivery speed and clarity.
- For SEO, finance, or medical sites: Google expects expertise, topical expansion, and structured interlinking. Content volume alone is not enough. Semantic consistency and authority matter more.
In thin-content niches, sites rank by utility. In expertise-driven domains, sites rank by depth, consistency, and credibility.
Conclusion
Knowledge domain is not just about picking a niche. It’s about owning it semantically, structurally, and authoritatively.
If you want your website to rank consistently:
- Define your knowledge domain clearly
- Publish structured content covering all related entities and attributes
- Align with Google’s Knowledge Base
- Help Google map your site into its Knowledge Graph
When this alignment happens, your brand moves from being a content publisher to a recognized entity within Google’s semantic architecture.
PRO TIP: Maintain 1 knowledge domain in single website
Disclaimer: This [embedded] video is recorded in Bengali Language. You can watch with auto-generated English Subtitle (CC) by YouTube. It may have some errors in words and spelling. We are not accountable for it.
