Search engines no longer match strings; they map things.
In the era of Semantic SEO, Google and other modern search engines process your content through Entity Recognition, Context Mapping, and Intent Resolution—not keyword frequency. This is why Entity-Based Content has emerged as a superior framework for content architecture, internal linking, and semantic indexing.
This guide explores how to build entity-rich pillar content, using examples from travel blogs (e.g., Paris Travel Guide) to demonstrate content structuring, semantic layering, and topical depth.
What Is Entity-Based Content?
Entity-Based Content is structured around real-world objects, people, places, concepts, and events—not arbitrary keywords. These are machine-readable units of knowledge connected in Google’s Knowledge Graph.
Entity Examples in a Travel Guide:
- Place Entities: Paris, France, Montmartre, Eiffel Tower
- Event Entities: Paris Fashion Week, Bastille Day
- Organization Entities: Louvre Museum, Air France
- Conceptual Entities: Solo Travel, Luxury Travel, Budget Itineraries
- People Entities: Couples, Honeymooners, Solo Travelers
These are not “related keywords.” They are semantic nodes that build contextual relationships, improving:
- Crawlability
- Indexing accuracy
- Ranking eligibility
- Feature snippet visibility
How to Structure an Entity-Based Article
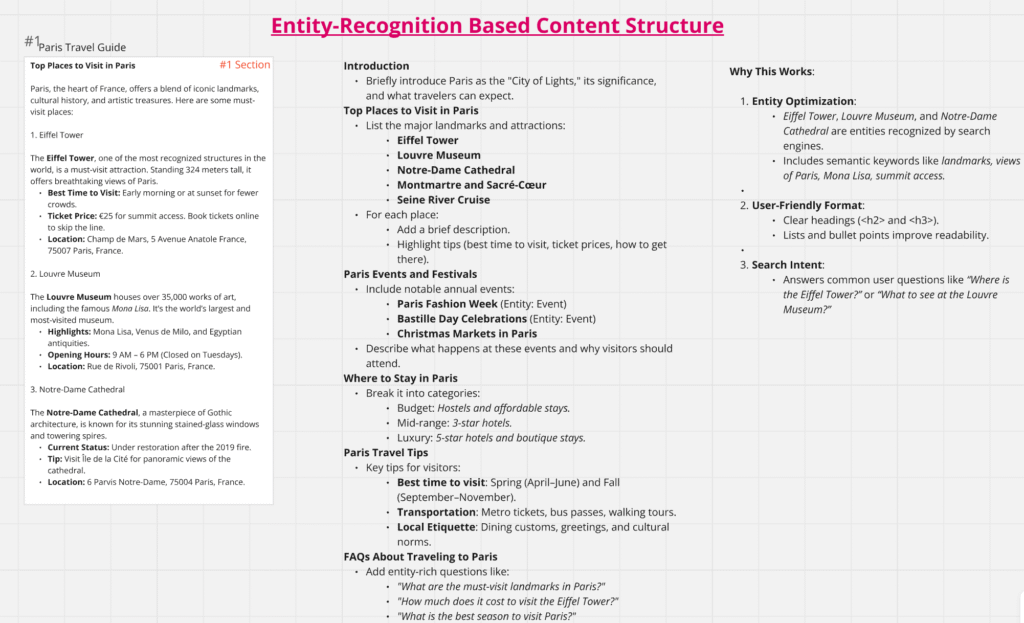
Let’s explore how to build a 5,000-word pillar page on the topic:
“Paris Travel Guide: Places, Events, Tips & FAQs”
ALSO READ …
- What is entity recognition in semantic
- What is entity and its types
- What is structured data
- What is entity attribute value
- How Google uses entities after extraction
Article Outline with Entity Mapping
| Section | Entity Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Introduction | Place / Concept | Define Paris as a city (not person), introduce its cultural and touristic significance |
| 2. Top Places to Visit in Paris | Place | Eiffel Tower, Louvre Museum, Montmartre, Notre Dame |
| 3. Events and Festivals in Paris | Event | Paris Fashion Week, Christmas Market, Bastille Day |
| 4. Where to Stay in Paris | Organization / Place | Budget hotels, mid-range, luxury, solo-traveler options |
| 5. Essential Travel Tips | Concept | Currency, safety, transportation (Uber, Metro), etiquette |
| 6. FAQ Section | NLP Targets | Structured for voice search + featured snippets |
| 7. Conclusion | Summary | Reinforce contextual relevance with call-to-action |
Also Read ..
Discover how to build entity-focused pillar pages
Entity Insertion Strategy by Section
Section 1: Introduction
- Disambiguate Paris by defining it explicitly as “capital of France in Europe”.
- Connect to France, Europe, and travel concepts like “city of light.”
Section 2: Top Places to Visit
Each place is a distinct entity with attributes:
@type: Landmark or Place- Attributes: ticket price, location, best visiting hours
Example Entities:
- Eiffel Tower (Landmark)
- Louvre Museum (Organization/Place)
- Montmartre (Neighborhood)
- Mona Lisa (CreativeWork → Painting → Louvre Exhibit)
Include:
- Ticket cost (user value)
- Optimal visiting time (contextual relevance)
- Location details (geo-coordinates, district)
Section 3: Events and Festivals
This section emphasizes temporal entities:
- Paris Fashion Week →
@type: Event - Bastille Day → Historical & Cultural Event
- Christmas Markets → Recurring Holiday Event
Structure with:
- Date range
- Audience type (tourists, families, solo travelers)
- Booking or registration resources
Section 4: Where to Stay
Include multiple user personas:
- Couples (entity: Person)
- Solo travelers (entity: Person)
- Luxury vs Budget (Concept → Service → Accommodation)
Semantic layer:
- Hotel name →
@type: Hotel - Mention booking platforms: Booking.com, Airbnb
Section 5: Essential Travel Tips
Functional entities for UX & SEO:
- Transportation: Uber, Metro, taxi →
@type: Organization - Currency: Euro →
@type: MonetaryUnit - Culture: “Bonjour” →
@type: Phrase, etiquette concepts - Scams: Pickpockets → Risk entity, security advisories
Tips should include both entity names and actions (e.g., “use contactless cards on RATP metro”).
FAQ Section: Structured for Search & Voice
Example Questions (Optimize with FAQPage schema):
- What are the top attractions in Paris?
- How much does it cost to visit the Eiffel Tower?
- What is the best time to travel to Paris?
- How to avoid pickpockets in Paris?
- Which events happen in Paris in summer?
Key Features:
- Answers should be concise, under 50 words.
- Include key entities and answer intents.
- Enables visibility in People Also Ask, Featured Snippets, and Voice Search.
Internal Linking & Topical Maps
Internal links should mirror your entity relationships:
| Anchor Text | Target Page |
|---|---|
| “Paris Packing List” | /packing-list-for-paris/ |
| “Paris Travel Tips” | /paris-travel-tips/ |
| “Events in Paris” | /events-in-paris/ |
| “New York Travel Guide” | /new-york-travel-guide/ |
Contextual anchors outperform generic terms. Avoid “click here”—use entity-aligned terms (e.g., “Explore more Paris events”).
Link structure must reflect semantic similarity, improving:
- Crawl depth
- Link equity distribution
- Topical authority
Schema Markup Recommendations
Article Schema:
{
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@type": "Article",
"headline": "Paris Travel Guide: Places, Events, Tips & FAQs",
"mainEntityOfPage": {
"@type": "WebPage",
"@id": "https://sahatravel.com/paris-travel-guide"
},
"author": {
"@type": "Person",
"name": "Saha"
},
"about": [
{"@type": "Place", "name": "Paris", "sameAs": "https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Paris"},
{"@type": "Event", "name": "Paris Fashion Week"},
{"@type": "Landmark", "name": "Eiffel Tower"}
]
}FAQ Schema (Voice + Featured Snippet Ready):
{
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@type": "FAQPage",
"mainEntity": [
{
"@type": "Question",
"name": "What is the best time to visit Paris?",
"acceptedAnswer": {
"@type": "Answer",
"text": "The best time to visit Paris is in spring (April to June) and fall (September to November)."
}
}
]
}Why Entity-Based Content Performs Better
| Factor | Advantage |
|---|---|
| Entity Density | Google better understands topical focus |
| Contextual Clarity | Disambiguates terms like “Paris” or “Eiffel” |
| Schema Integration | Eligible for Rich Results |
| Voice & Zero-Click Optimization | FAQ + Snippets = Higher CTR |
| Internal Topical Map | Strengthens authority in content cluster |
Unlike keyword-stuffed content, entity-based articles scale with algorithms like:
- Hummingbird: Entity + Intent Matching
- BERT/MUM: Contextual embeddings
- Knowledge Graph: Relationship resolution
Conclusion: Think in Entities, Not Keywords
“Keywords describe words. Entities describe knowledge.”
Entity-Based Content is not just an SEO technique—it’s how you build trust in the language of search engines. If your content doesn’t reflect real-world entities, relationships, and structures, it will be contextually invisible.
Focus on:
- Entity recognition
- Schema markup
- Internal entity relationships
- Topic clusters and subpages
Here’s the Full Content Outline & It’s Content »> Copy Here
Disclaimer: This [embedded] video is recorded in Bengali Language. You can watch with auto-generated English Subtitle (CC) by YouTube. It may have some errors in words and spelling. We are not accountable for it.
